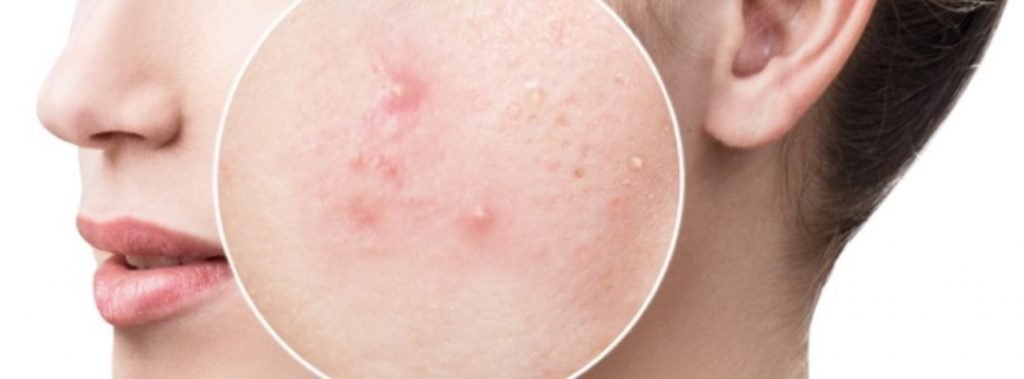
Acne is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that causes spots and pimples, especially on the face, shoulders, back, neck, chest, and upper arms.
Whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, cysts, and nodules are all types of acne.
It is the most common skin condition. It commonly occurs during puberty, when the sebaceous glands activate, but it can occur at any age. It is not dangerous, but it can leave skin scars. The glands produce oil and are stimulated by male hormones produced by the adrenal glands in both males and females.
At least 85 percent experience acne between the ages of 12 and 24 years.
Fast facts on acne
Here are some facts about acne. More detail is in the main article.
- Acne is a skin disease involving the oil glands at the base of hair follicles.
- It affects 3 in every 4 people aged 11 to 30 years.
- It is not dangerous, but it can leave skin scars.
- Treatment depends on how severe and persistent it is.
- Risk factors include genetics, the menstrual cycle, anxiety and stress, hot and humid climates, using oil-based makeup, and squeezing pimples.
Home remedies
There are many suggested home remedies for acne, but not all of them are supported by research.
Diet: It is unclear what role diet plays in worsening acne. People who consume a diet that offers a good supply of vitamins A and E and of zinc may have a lower risk of severe acne. Acne and diet as “controversial,” but a diet with a low glycemic load may help.
Tea-tree oil: Tea-tree oil may help treat mild to moderate acne.
Tea: There is some that polyphenols from tea, including green tea, applied in a topical preparation, may be beneficial in reducing sebum production and treating acne. However, the compounds in this case were extracted from tea, rather than using tea directly.
Moisturizers: These can soothe the skin, especially in people who are using acne treatment such as isotretinoin, say researchers. Moisturizers containing aloe vera at a concentration of at least 10 percent or witch hazel can have a soothing and possibly anti-inflammatory effect.

Causes
Human skin has pores that connect to oil glands under the skin. Follicles connect the glands to the pores. Follicles are small sacs that produce and secrete liquid.
The glands produce an oily liquid called sebum. Sebum carries dead skin cells through the follicles to the surface of the skin. A small hair grows through the follicle out of the skin.
Pimples grow when these follicles get blocked, and oil builds up under the skin.
Skin cells, sebum, and hair can clump together into a plug. This plug gets infected with bacteria, and swelling results. A pimple starts to develop when the plug begins to break down.
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is the name of the bacteria that live on the skin and contributes to the infection of pimples.
The severity and frequency of acne depend on the strain of bacteria. Not all acne bacteria trigger pimples. One strain helps to keep the skin pimple-free.
Hormonal factors
A range of factors triggers acne, but the main cause is thought to be a rise in androgen levels.
Androgen is a type of hormone, the levels of which rise when adolescence begins. In women, it gets converted into estrogen.
Rising androgen levels cause the oil glands under the skin to grow. The enlarged gland produces more sebum. Excessive sebum can break down cellular walls in the pores, causing bacteria to grow.

Other possible triggers
Some genetic factors may increase the risk.
Other causes include:
- some medications that contain androgen and lithium
- greasy cosmetics
- hormonal changes
- emotional stress
- menstruation
Treatment
Treatment depends on how severe and persistent the acne is.
Mild acne
Mild acne can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, such as gels, soaps, pads, creams, and lotions, that are applied to the skin.
Creams and lotions are best for sensitive skin. Alcohol-based gels dry the skin and are better for oily skin.
OTC acne remedies may contain the following active ingredients:
- Resorcinol: helps break down blackheads and whiteheads
- Benzoyl peroxide: kills bacteria, accelerates the replacement of skin, and slows the production of sebum
- Salicylic acid: assists the breakdown of blackheads and whiteheads and helps reduce inflammation and swelling
- Sulfur: exactly how this works is unknown
- Retin-A: helps unblock pores through cell turnover
- Azelaic acid: strengthens cells that line the follicles, stops sebum eruptions, and reduces bacterial growth. There is cream for acne, but other forms are used for rosacea.
It is advisable to start with the lowest strengths, as some preparations can cause skin irritation, redness, or burning on first use.
These side effects normally subside after continued use. If not, see a doctor.
Treating moderate to severe acne
A skin specialist, or dermatologist, can treat more severe cases.
They may prescribe a gel or cream similar to OTC medications but stronger, or an oral or topical antibiotic.
Corticosteroid injection
If an acne cyst becomes severely inflamed, it may rupture. This can lead to scarring.
A specialist may treat an inflamed cyst by injecting a diluted corticosteroid.
This can help prevent scarring, reduce inflammation, and speed up healing. The cyst will break down within a few days.