It is common knowledge that a strong immune system offers protection against viruses and diseases, while a weak one makes you more susceptible to catching a cold or worse. But what exactly is it and how does it work?
Immunity refers to the body’s ability to prevent the invasion of pathogens. Pathogens are foreign disease-causing substances, such as bacteria and viruses, and people are exposed to them every day. Antigens are attached to the surface of pathogens and stimulate an immune response in the body. An immune response is the body’s defense system to fight against antigens and protect the body.
There are several types of immunity, including innate immunity, passive immunity, and acquired/active immunity. is a visual showing active immunity as a process of exposing the body to an antigen to produce an adaptive immune response, while passive immunity “borrows” antibodies from another person.
The definition of immunity
Simply put, immunity is your body’s ability to resist toxins, infections and other harmful substances or microorganisms with the use of sensitized white blood cells or specific antibodies. Think of it as a protection system – this is how your body defends itself. If it wasn’t for the immune system, various bacteria, viruses and even fungi could attack or infect your body at will. Thanks to immunity, that’s not the case.
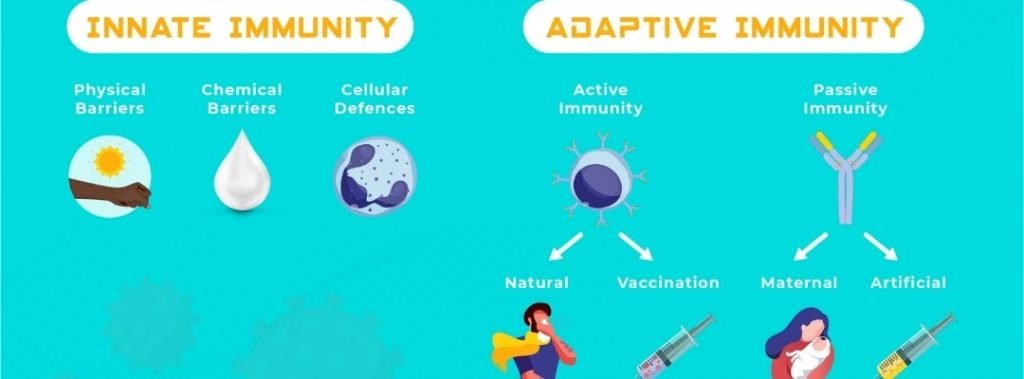
Different types of immunity
There are 4 types of immunity – 3 natural and an additional one:
- Innate immunity – the one we are born with. This is our innate immune system. It varies in strength; some people are born with a strong immune system, while some are born with a weak immune system.
- Adaptive immunity – also called “acquired immunity”. The adaptive immune system protects us based on its past “experience”. This is why, after being infected with something and getting better, we are no longer (at least for some time) susceptible to the same infection.
- Passive immunity – temporary immunity, also called “borrowed immunity”. This is an immunity which we gain from another person, i.e. a child borrowing temporary immunity from the mother through her breast milk.
- Immunizations – we can be made immune to something – typically through the administration of a vaccine.
The purpose and functions of the immune system
The main function of the immune system is to protect you from harmful microorganisms that may cause infections. However, it doesn’t stop at prevention – if you do get sick, it is your immune system that is your body’s first line of defence. It will fight the infection and act to minimize the damage done to your body. A healthy immune system will be able to fight off most infections. A weakened immune system means your illness can last longer, and symptoms may be more severe.

How to bolster your immune system
A healthy lifestyle is the best immune booster. It’s always a good idea to ensure you look after your immune system on a daily basis. Below you will find a few tips on how to keep your immune system healthy and strong through everyday activities1. Remember that if you think your immunity might be weakened, you should always consult your doctor.
- Eat a balanced diet, including lots of fresh fruit and vegetables. A healthy diet will provide essential vitamins and minerals your immune system needs to function properly.
- If you are not sure you are getting enough vitamins and minerals in your diet, consider adding a supplement that can help strengthen your immune system2.
- Get regular exercise. This will help reduce stress, which negatively affects immunity, and improve blood circulation, allowing white blood cells to reach any cells affected by disease.
- Take steps to reduce stress. If you find you are under persistent stress, you can try meditation techniques or yoga.
- Get quality sleep. Rest allows your body to regenerate and helps your immune system to work adequately.
- Maintain a healthy weight. People who are overweight have weakened immune function, which can make them more at risk of catching illnesses.4
- Get proactive to avoid infection. Wash your hands thoroughly and regularly, avoid sharing personal items if sharing space with an infected person and make sure any meat you eat is properly cooked.
- Don’t smoke. Smoking tobacco is harmful to your immune system and can make it less effective at fighting diseases.